Prime Numbers
Prime numbers are those that can only be divided by themselves and one. They are the foundation for our number system and can be found in nature, art, and music.
The first prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, and 13. But there are infinitely many prime numbers! The largest known prime number is 274,207,281-1. It’s a whopper!
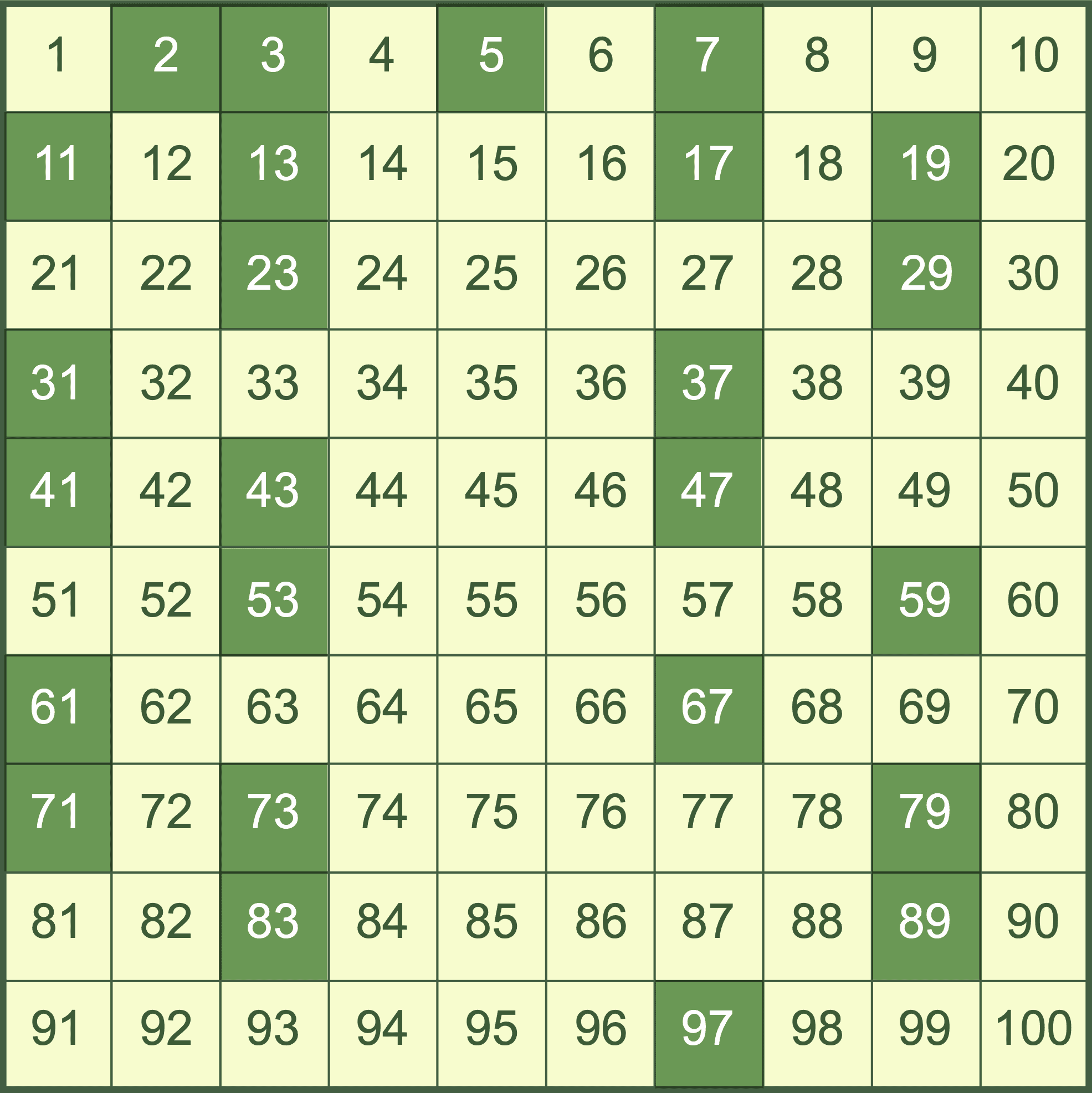
Prime numbers have fascinated mathematicians for centuries. They are full of patterns and mysteries. For example, the prime numbers seem to be randomly distributed, but there are actually more primes than can be expected by chance.
And there are infinitely many twin primes, a pair of prime numbers that differ by 2. (For example, 3 and 5 or 11 and 13.)
Program Code
num = int(input("Enter a number: "))
# prime numbers are greater than 1
if num > 1:
# check for factors
for i in range(2,num):
if (num % i) == 0:
print(num,"is not a prime number")
break
else:
print(num,"is a prime number")
# if input number is less than
# or equal to 1, it is not prime
else:
print(num,"is not a prime number")Example 1:
Input Given:
Enter a number: 3
Output Expected:
3 is a prime number
Example 2:
Input Given:
Enter a number: 69
Output Expected:
69 is not a prime number
Code Explanation
- We are taking input from the user and storing it in the variable num.
- Then we check if the number is greater than 1.
- We then use a for loop to check if the number is divisible by any number between 2 and itself.
- If the number is divisible by any number between 2 and itself, we are printing that the number is not a prime number.
- If the number is not divisible by any number between 2 and itself, we are printing that the number is a prime number.
- If the number is less than or equal to 1, we are printing that the number is not a prime number.