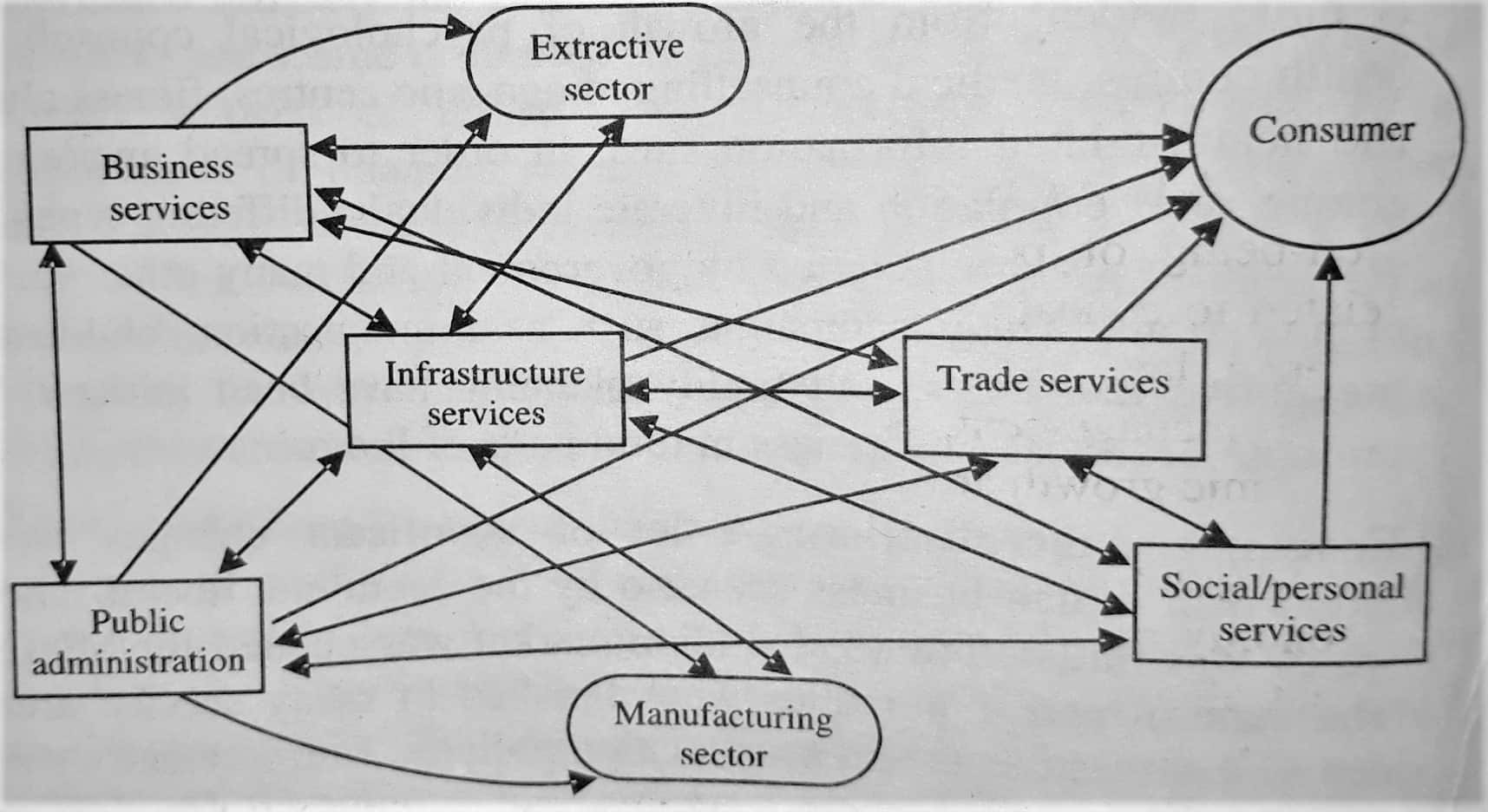
Services are the most significant element of various economic activities within a society. The economic model, depicted in the figure below, was formulated by Dorothy Riddle to illustrate the importance of the service sector in global development.
This economic model represents the flow of different economic activities among the three crucial sectors of the economy: manufacturing, extractive (encompassing mining and farming), and services. The service sector is further divided into five sub-groups. The consumer is the ultimate endpoint of all these activities.
The below-stated points can be used to have complete knowledge about the role of the service sector in an economy:
1. Infrastructure Services
Infrastructure services form a critical pillar of the economy. These services encompass transportation and communication, serving as a vital link across all sectors. Additionally, they facilitate connections with customers. Infrastructure and trade services function as intermediaries between the manufacturing, mining, and distribution sectors. These services are indispensable for industrialisation, and without them, societal progress cannot be achieved.
2. Business Services
Business services encompass areas such as banking, finance, advertising, consulting, and other business functions. These services are provided by specialist firms to manufacturing companies at reasonable costs. While manufacturing firms have the option to manage these services in-house, the associated costs can be prohibitive. Therefore, they often choose to outsource services such as banking, advertising, and consulting to firms that specialise in these areas.
3. Trade Services
Trade services encompass activities such as retailing, repair, and maintenance. These services are vital for the smooth functioning of society and for enhancing the quality of life. For instance, consider the significance of transportation for distributing food across various locations or banking services for fund transfers – their importance is undeniable.
Healthcare, restaurants, and so on are parts of social or personal services. The household activities have moved into the economy, like lodging, cleaning, child care, restaurants, and many more.
5. Public Administration
Public administration encompasses a variety of services pivotal to societal well-being and progression. These include, but are not limited to, education, environmental management, electricity provision, water supply, healthcare, defence, law enforcement, public transportation, town planning, social services, and waste management. A stable investment environment and consistent economic growth are facilitated by effective public administration.
Consequently, it becomes abundantly clear that services are not merely supportive activities but form the core of any economy. They are crucial components necessary for building a robust economy. The service sector not only assists but also synergizes with the manufacturing and mining sectors in output production. Services hence play an instrumental role in shaping a global economy.