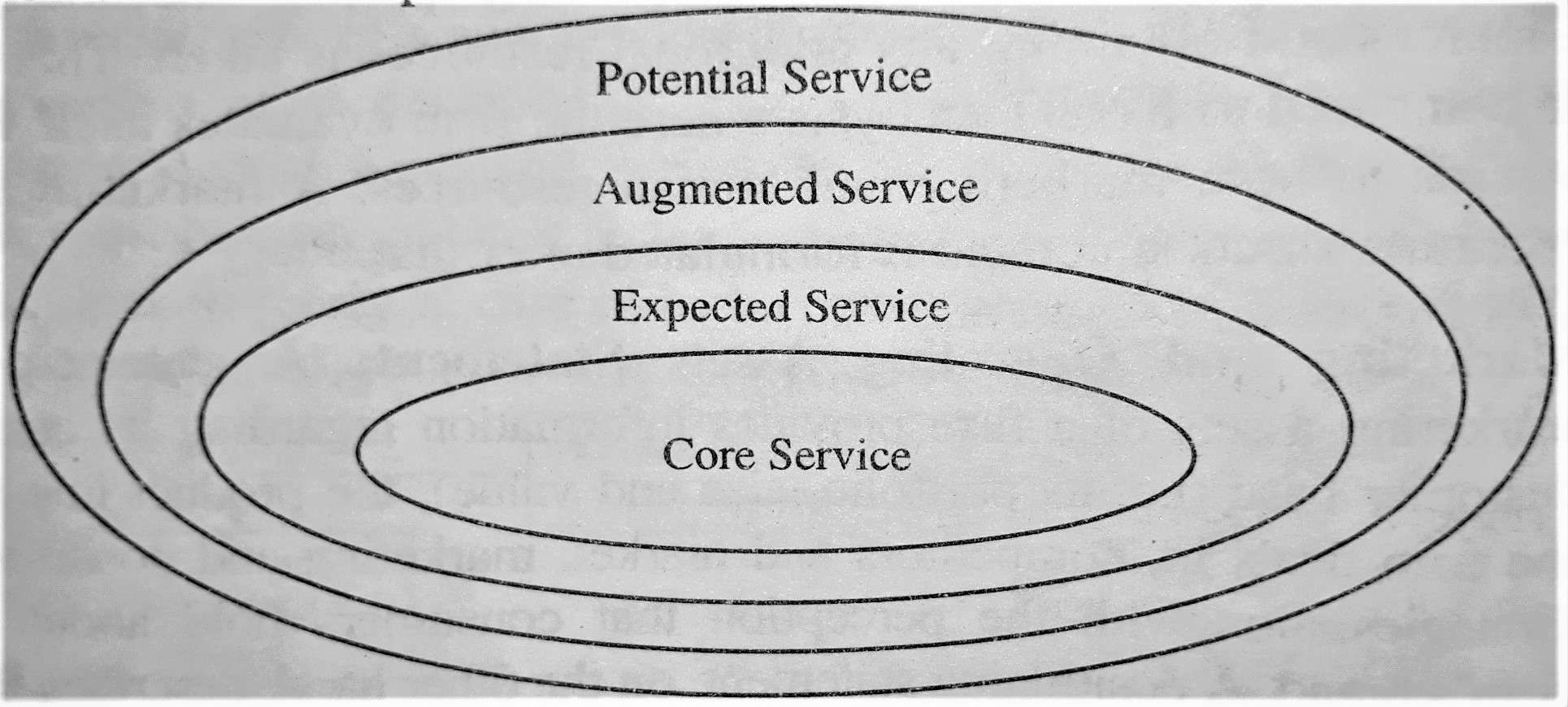
The levels of service product are as follows:
1) Core Service: Core benefit is the most important level of the hierarchy. At this level, the customer is buying the essential benefit or service. Here, marketers are the benefits providers to customers.
For example, a hotel guest is buying rest and sleep; a woman at a spa resort is buying comfort and luxury.
2) Expected Service: At this level, the marketer needs to prepare an expected service. An expected service comprises of all those attributes which a customer expects while buying a service.
For example, a restaurant’s visitor expects a clean table, good quality food, quick services, and a vibrant ambiance. Mostly, all restaurants try to provide these attributes, but customers also look for the least expensive restaurant and these attributes.
3) Augmented Service: The third level of service provides augmented service to its customers, which is beyond their expectations. These types of services have additional attributes and benefits which enable the customers to differentiate between the available service and other services offered by competitors.
For example, a hotel may include fine dining and 24×7 room service, fresh flowers, a remote-control television set, rapid check-in and express check-out, which are all extended services provided by the hotel to build up an augmented service.
4) Potential Service: The last and the fourth level is that which offers the potential service. This type of service covers all the prospective alterations and extensions that the service may go under in the future. At this level, the companies make most of their efforts to find out new ways to gratify their customers and offer unique services to them.
For example, an innovative transformation of the traditional hotel service can be like offering all-suite hotels where the occupant books a set of rooms.