The response of an organization to a service failure through taking suitable actions is known as Service recovery.
It is a planned attempt made by a service organization to convert a dissatisfied or aggrieved customer into a satisfied one so that he/she continues to do business with the organization.
It is regarded as a positive method to handle customer complaints. This is because complaint handling holds significant negative underlying implications, while these are positive in the case of service recovery.
Complaint handling, however, attempts to pacify or conciliate a customer, thereby reducing its negative implications.
On the other hand, service recovery tries to develop a positive relationship with the customers and realizes their latent potential and value to the organization.
Finding remedial solutions to current poor situations and converting customer dissatisfaction into satisfaction are the two main motives for service recovery.
A hit-or-miss approach is usually avoided in the service recovery process and instead, a planned and organized approach is adopted.
Thus, service firms usually integrate a service recovery management system into their cultural policies so as to master the service recovery process and eliminate mistakes.
For effective service recovery management, the commitment of top management is essential regarding the integration of service logic, shared values, and strategy along with the sharing of user data and recovery rewards.
Such integration will have the potential to generate best practices in the service recovery management system.
Also, it will help the service firm to achieve greater profits, higher customer loyalty, and greater customer satisfaction.
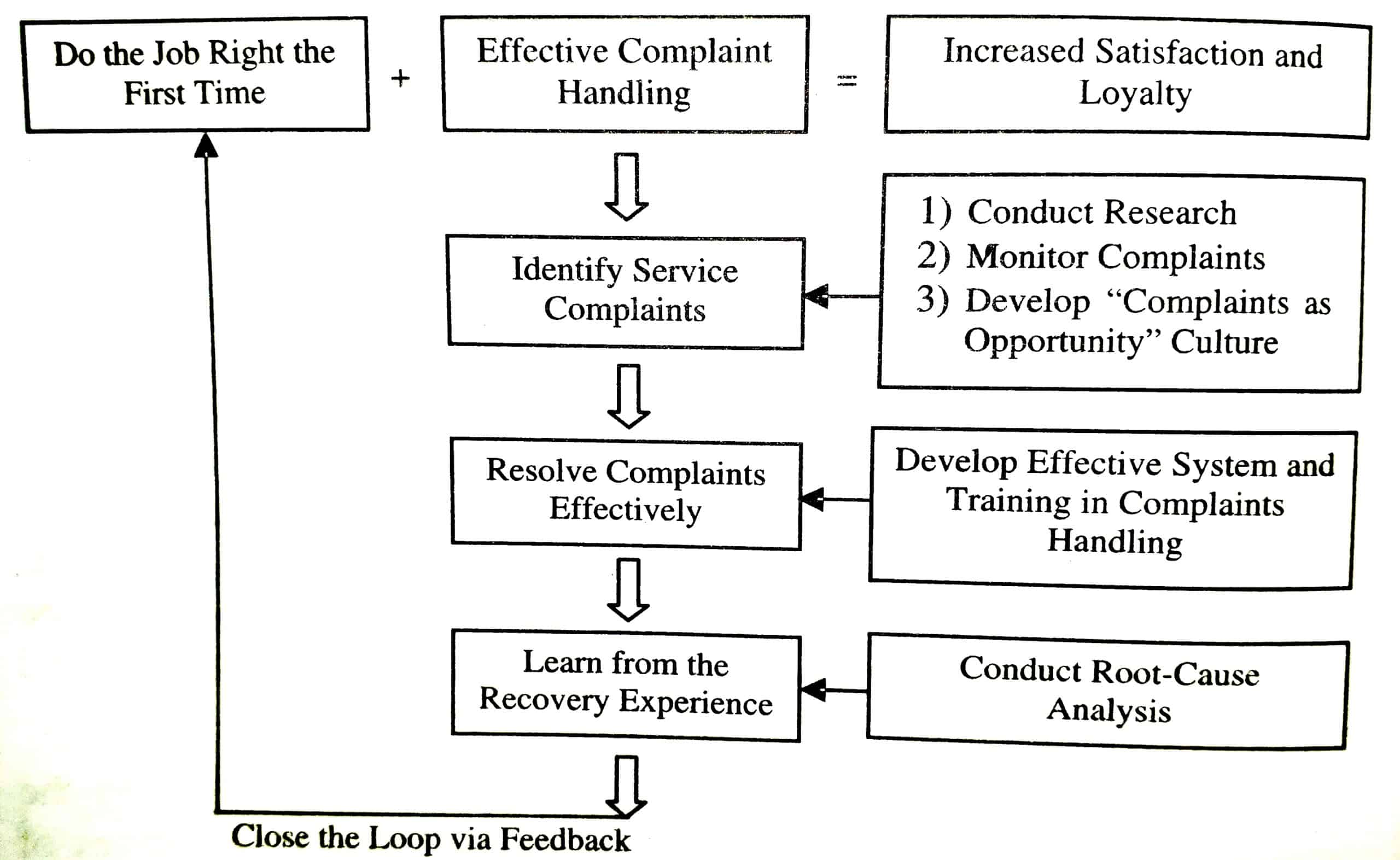
Principles of an Effective Service Recovery
The figure given below illustrates the principles of an effective service recovery, which are explained as follows:
Make it Easy for Customers to Give Feedback
Managers can deal with the reluctance of disappointed customers by directly addressing the causes of their reluctance.
Lately, the complaint-gathering efforts of many service firms have been fortified as they have included new facilities for customers like toll-free numbers, web links, customer comment cards, video terminals for recording feedback/complaints, etc. in order to give their feedback more easily.
Also, most of the firms feature their improvements in service delivery through customer newsletters showing that they have responded to the customers’ feedback and complaints.
Enable Effective Service Recovery
It takes more than virtuous determination or expression to provide remedial solutions for customer problems.
For an effective service recovery, proper commitment, planning, and the right set of policies are required. The following points are mentioned in this regard:
Service Recovery should be Proactive
There should be an immediate generation of service recovery, i.e., customers should not get a chance to complain about anything.
The frontline service staff should thoroughly know the signs of disappointment and should ask the customers if they are facing any issues.
For example, a waiter in a restaurant upon seeing that the customer has finished only half of what he ordered, he can ask whether he liked that item or not or why he hasn’t finished his meal.
The response of frontline staff after the response of the customer will determine the extent of our service recovery.
If the customer responds that he did not fife what he orders, the waiter has a chance for service recovery by giving him a supplementary dessert or discount on his next visit.
Recovery Procedures Need to be Planned
There should be contingency plans made for service failures.
These plans become more important for cases that happen more frequently and which are not possible to design out of the service delivery system.
For example, very often, the policies of revenue management in the hospitality and tourism industries result in overbooking conditions where travelers do not have access to boarding at hotels.
In such conditions, they have to walk away dissatisfied even if they had reservations. There should be contingency plans for such circumstances.
Recovery Skills must be Taught
When things do not work as planned like in a service failure, the customers start feeling insecure and disappointed.
In such conditions, they seek immediate assistance from the frontline staff. These are the situations where the response of the frontline staff determines the effectiveness of service delivery.
Therefore, effective training must be given to the frontline service staff so that they can transform customers’ strife into satisfaction.
Recovery Requires Empowered Employees
The activities and efforts of service recovery should be flexible in nature.
The frontline personnel should be authorized to use their communication skills and judgment for developing on-the-spot solutions to customer problems.
This becomes quite essential in cases of non-ordinary failures. When employees are empowered with decision-making authority, the chances of recovering customer goodwill increase.
Anticipate the Needs for Recovery
Usually, the employees or people related to a new product or service know its drawbacks and potential issues that might occur while delivering.
The need for recovery must be anticipated and service firms must realize the fact that even the best service delivery system can fail at some point in time.
By anticipating the potential issues, service firms can prepare alternative solutions so that no customer complains about similar issues.
For example, it may happen that customers in a restaurant may require warm water for the purpose of drinking and not regular water.
Keeping the customer waiting for warm water might create disappointment; while keeping warm water ready at all times may delight customers with similar needs.
Quick Decision-Making and Fast Response
Responding quickly to customers is one of the key success factors to retain customers.
Although the frontline staff may already be responding as quickly as they can, the entire organization dealing with the process of service recovery must be designed for flexibility and swiftness.
Such an organization includes direct decision-making and clear-cut goals. The fastest decision-making can be achieved by a service firm when it empowers its frontline staff with the authority to make decisions.
Therefore, the ultimate objective is not to describe the growth processes in a better form but to describe activities and procedures that empower the frontline personnel with decision-making authorities,
Train Employees
The service firm should make sure that the training programs of frontline personnel include both lessons on service delivery as well as lessons on service recovery.
This is because if anything goes wrong, the frontline personnel are the one that deals with customer disappointment. These strategic initiatives are significant for describing the service recovery programs’ long-term direction.
This comes in handy when a customer initiates to contact the service firm and dis^^H problems along with its solutions.
How Generous should Compensation be
There are numerous costs linked with several service recovery strategies. The following points help the managers to decide the amount of compensation that the firm must offer against a service failure:
What is the Positioning of the Firm
The managers should analyze the firm’s positioning. If the firm has established its marketplace due to its excellence in service delivery and charges high prices for service quality, then the customers will expect that there will be no service failure.
Under such conditions, the service firm must make a noticeable effort for recovering the rare failures and become well-prepared for offering compensation having significant value for the customer.
However, in the case of a small service marketplace, offering a free dessert or coffee can be considered as compensation.
How Severe was the Service Failure
This works on the principle that the punishment should suit the crime. The managers should analyze how severe the service failure to customers is.
Little inconveniences can be avoided but a major problem in terms of effort, annoyance, time, money, etc., demands worthy compensation.
Who is the Affected Customer
Those customers who have long-term relations with the firm or those who purchase | premium services or spend heavily tend to expect more from the service provider.
From the view of the service provider, giving good and fair compensation to such customers is worth it for growing the business.
Therefore, compensation should always be fair; not big or small. The chances that a first-time customer will become a repeat customer increases when he is treated well for the first time.
Well-dosed generosity should be the overall rule for compensation. The service firm should also know that overly-generous compensations are also undesirable.
Such compensations create suspicious thoughts in customers’ minds as they doubt the company’s underlying aims.
Moreover, customers raise questions about the ethicality of the business. Over-generous compensations also do not promise repeat purchases or long-term customer engagement. Therefore, compensation should be fair in every aspect.
Service Recovery Strategies
Recognizing customers’ problems and addressing them to their satisfaction so as to promote customer retention is the basic aim of service recovery.
But, service recovery does not happen by itself; it is an organized business activity that demands proper design and implementation.
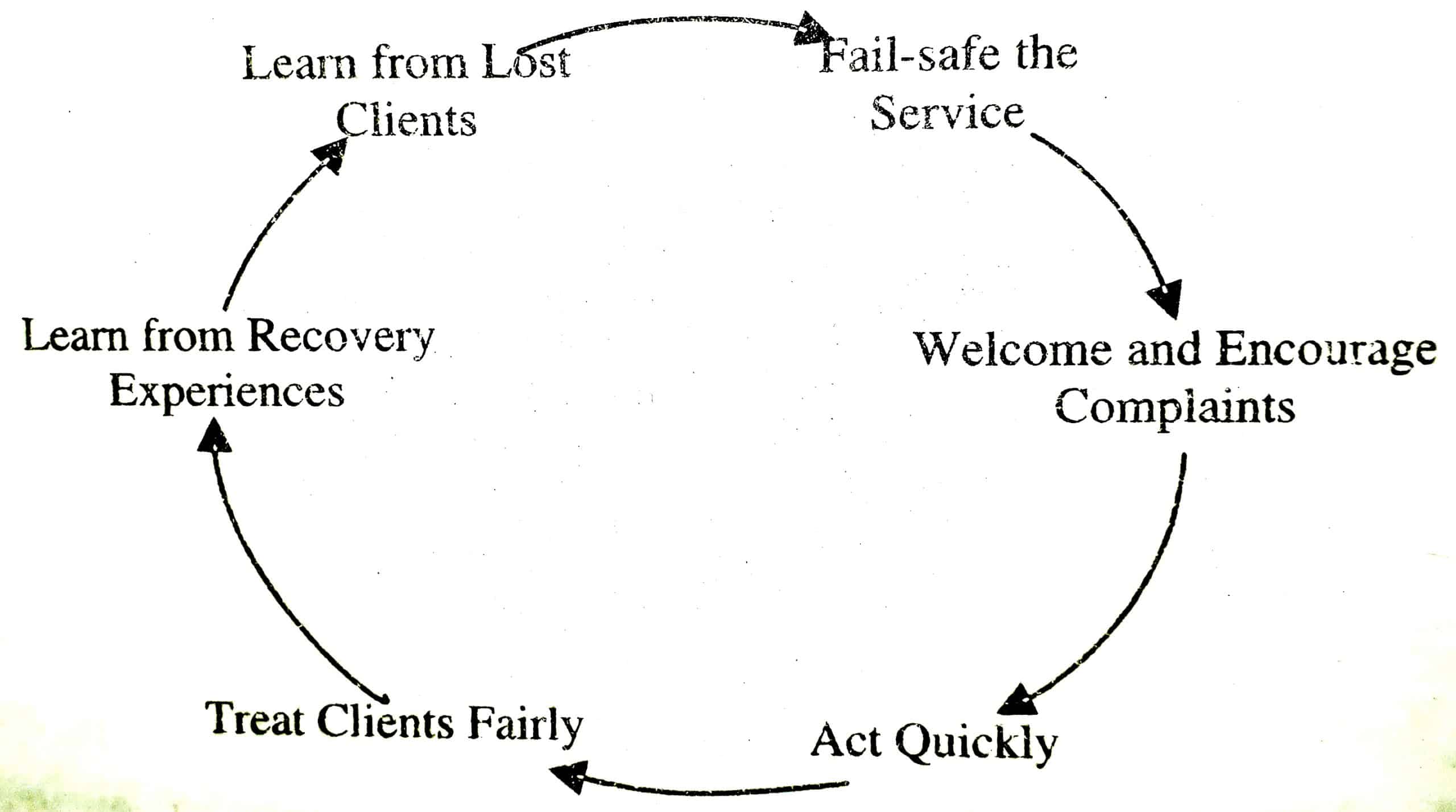
For this purpose, Zeithaml and Bitner have recognized some fundamental strategies which are helpful for service providers.
These six strategies are illustrated in the figure given below in the form of a continuous circle:
Fail-Safe the Service – Do it Right the First Time
This strategy states that there will be no need for service recovery if the service is delivered without any mistakes for the first time.
However, doing right for the first time is much easier to say than do.
Welcome and Encourage Complaints
There should be efforts made towards stimulating customers to make complaints in order to recognize the service issues.
For this purpose, the process of making a complaint should also be made easier.
Act Quickly
When a customer makes a complaint, immediate action must be taken. Customers become even more disappointed when they see that their complaints are not heard correctly or no action has been taken.
As a result, the customer will switch to a different service provider and will spread negative word-of-mouth.
In order to avoid this, it is important that customer-contract employee is empowered with making suitable decisions when required in order to act quickly upon the complaints.
Treat Clients Fairly
Clients make complaints because they seek fair treatment. All they need is a justifiable solution to their problems.
Therefore, the solution offered to them must be equivalent to the original service. Many times, customers are offered discount coupons and special offers as a token of the inconvenience caused.
Learn from Recovery Experiences
A service firm can easily identify the main issues in its service delivery by focusing on the common complaints made by the customers.
Also, the underlying reasons for such issues can also be identified by effectively monitoring the activities of service recovery.
In this way, the quality of the overall service delivery system can also be enhanced. Hence, complaints are helpful for a service firm to improve the quality of its service delivery and offerings.
Learn from Lost Clients
A customer who switched to another service provider acts as a source of potential information that helps the company to improve and learn from its past mistakes,
There are following three additional service recovery strategies along with the six strategies given by Zeithaml and Bitner:
1. Reflect that You Understand Issues from every Customer’s Viewpoint: The only way to understand the reasons for customer disappointment is by understanding the issues from the viewpoints of the customers.
The frontline service employees must not jump directly to self-made conclusions.
2. Do not Argue with Customers: One should never make unnecessary arguments with the customers as it makes the situation worse and irritates customers to a greater extent.
The main aim is to collect information regarding their disappointment and arrive at a solution that is mutually acceptable.
3. Keep Customers Informed of Progress: Customers do not like to leave in the dark; they are eager to know about the progress.
Keeping customers informed about the progress status and reports helps in reducing their level of stress and worries.
Service Recovery Process
The process of service recovery includes four steps as shown in the table given below:
| Consumer Service Example | Business-to-Business Service Example | |
| Step 1: Create a service recovery program. | A fitness center calls to all of its members to know whether they want to renew or end their membership. | A bike rental business has made contracts with a repair service provider for dealing with any emergency problems in the vehicles. |
| Step 2: Motivate customers to file complaints. | The center calls 30 members every month in order to know their satisfaction level. Also, the members who do not wish to renew their membership are requested to give their feedback or make complaints so as to know their reason for discontinuation. | Every month, 5 random customers are contacted to give feedback regarding service delivery. If they are not satisfied, they are urged to complain. |
| Step 3: Use the information obtained from service failures to decrease service issues. | The information obtained from the members in the form of feedback and complaints is forwarded to the management and is discussed thoroughly. | The survey information is timely given to all branches in. |
| Step 4: Service firms allocate suitable resources to the process of service recovery. | The responsibility of service recovery is delegated to a capable employee or team. | Articles related to effective service delivery and service recovery are included in every company’s newsletter. Similar topics are also discussed in management meetings. |
Significance of Service Recovery
The significance of service recovery is explained as follows:
1. Building Customer Loyalty
The probability of establishing positive intentions of customer loyalty is increased with a ‘bit extra’ care provided after a service failure.
It is considered an important factor in the development of customer loyalty. A second goal can be providing value-added compensation.
2. Increasing Customer Satisfaction
The chances of converting dissatisfied customers into satisfied customers increase with the help of effective service recovery.
This is certainly important for maintaining a healthy and profitable business in the marketplace.
3. Greater Customer Retention
Customers that complain about service delivery and obtain an effective service recovery usually have a positive attitude toward the service provider.
Service firms have now begun to include and integrate the policies of service recovery into their customer retention policies.
4. Developing Higher Repurchase Intention
There are connections to service recovery with word-of-mouth intentions and repurchased behavior.
A dissatisfied customer who has experienced a service failure will share his/her bad experience with everyone else.
Thus, service recovery linked with satisfaction is a significant mediator between posts and traits of service recovery.
5. Positive Customer Perception
The perception of customers regarding service recovery is greatly influenced by restitution, compensation, and the manner in which it is delivered, i.e., the response of frontline staff to customers.
6. Generate Positive Word of Mouth
Service recovery generates positive word-of-mouth in a similar way to a dissatisfied customer creates negative word-of-mouth.
7. Increased Profits
The superior traits of service delivery present in a service recovery make the customer more satisfied and happy.
This will create a bond between the customer and the firm and significantly help in maintaining the long-term relationship.
Happy customers are often ready to pay for premium services which are profitable for the service organizations and create a win-win situation for both parties.